How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many ask before taking to the skies. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and understanding controls to mastering flight planning and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, ensuring you’re well-equipped to confidently pilot your drone and capture breathtaking visuals.
Understanding the legal and regulatory aspects is also crucial, so we’ll explore those important considerations to ensure safe and compliant operation.
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach, breaking down complex concepts into easily digestible information. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the exciting world of drone piloting.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring both the safety of the drone and the surrounding environment. This involves checking key components, verifying GPS signal strength, and understanding potential environmental factors.
Pre-flight Inspection and Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist minimizes risks and helps identify potential issues before they escalate. The following steps should be followed meticulously before every flight:
| Item | Check | Notes | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge? | Ensure battery is fully charged and within recommended voltage range. | Replace if necessary. |
| Propeller Condition | Inspect for cracks or damage. | Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal Strength | Strong signal? Sufficient satellites? | At least 6-10 satellites are recommended for stable flight. | Relocate to an area with better signal if necessary. |
| Gimbal Function (if applicable) | Smooth movement? | Check for any unusual noises or vibrations. | Calibrate if needed. |
| Camera Functionality | Lens clear? Image preview accurate? | Clean the lens if necessary. | Adjust camera settings as required. |
| Flight Environment | Wind speed? Obstacles? Airspace restrictions? | Avoid flying in high winds or near obstacles. Check for no-fly zones. | Postpone flight if conditions are unsafe. |
| Emergency Procedures | Familiar with return-to-home function? | Ensure you understand how to execute an emergency landing. | Review emergency procedures before each flight. |
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Procedures
Launching and landing a drone safely requires awareness of the surrounding environment and adherence to best practices. Different environments demand different approaches.
- Windy Conditions: Launch and land into the wind to maintain stability. A slight headwind is preferable.
- Confined Spaces: Ensure ample space for maneuverability and avoid obstacles. Practice precise hovering and control.
- Open Areas: Choose a level, clear area free of obstructions. Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
- Near Water: Always have a backup plan in case of unexpected events. Consider using flotation devices for added safety.
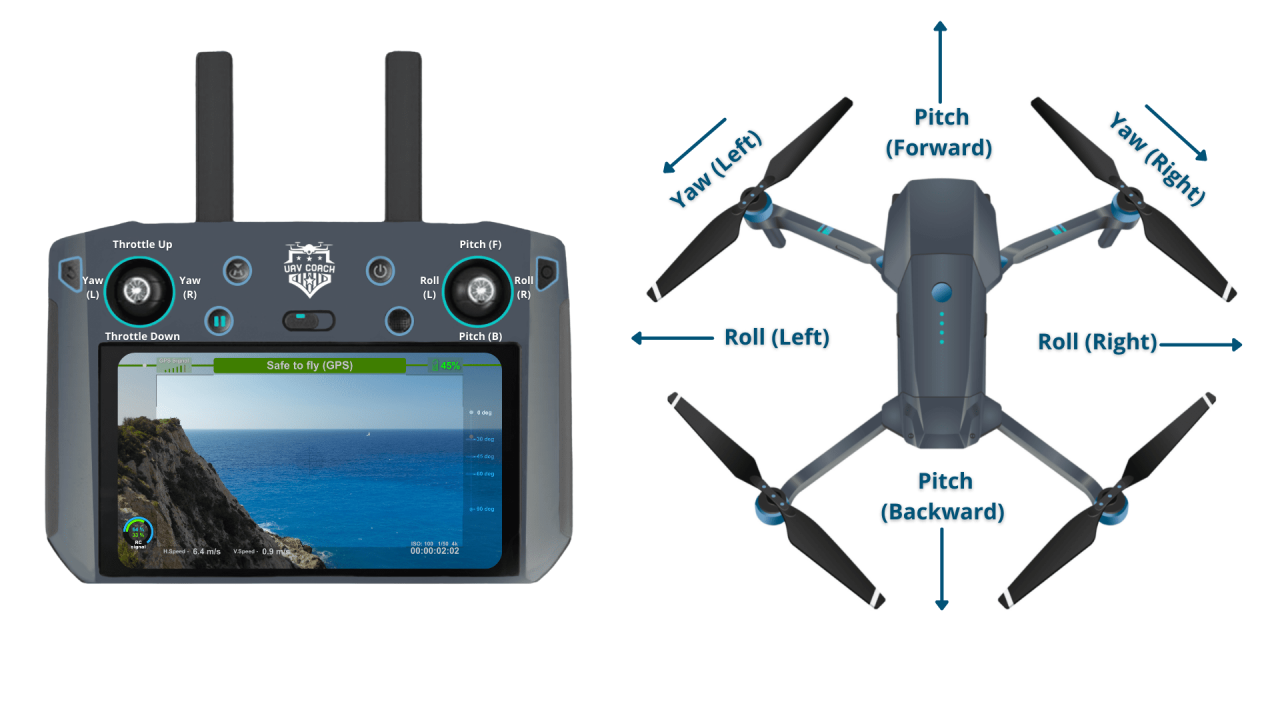
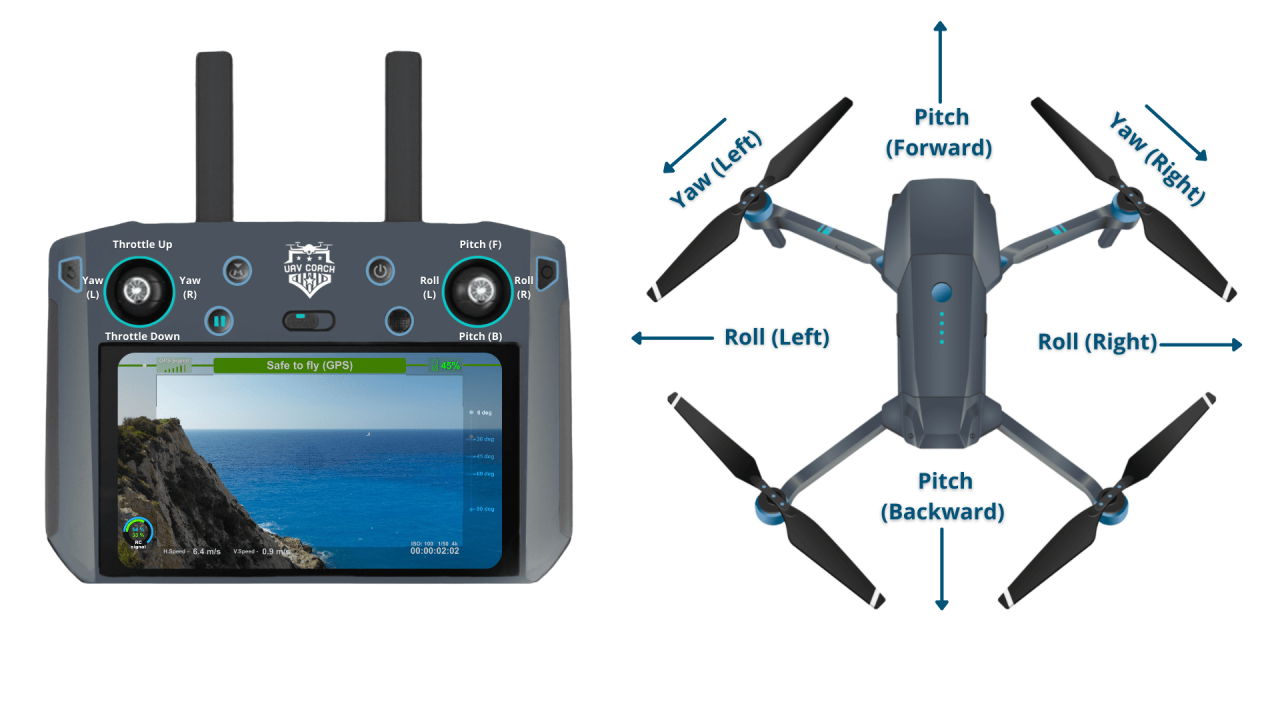
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Effective drone operation hinges on a clear understanding of its controls and various flight modes. Each mode offers different levels of autonomy and control, suitable for various situations and skill levels.
Drone Controls and Their Functions
Most drones use two joysticks or control sticks. One typically controls the drone’s altitude and movement forward/backward, while the other controls yaw (rotation) and left/right movement. Buttons and switches control additional functions like camera settings and return-to-home.
Flight Modes and Their Applications
Different flight modes offer varying degrees of control and stability. Understanding their nuances is critical for safe and efficient operation.
- GPS Mode: Maintains position and altitude using GPS data. Ideal for stable, long-range flights.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation (pitch, roll, yaw) relative to its current position. More responsive than GPS mode but requires more skill.
- Manual Mode: Offers direct control over all aspects of the drone’s movement. Requires advanced piloting skills.
Altitude, Heading, and Speed Control

Precise control over altitude, heading (direction), and speed is paramount for successful drone operation. These parameters directly impact image quality, flight safety, and mission completion.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as takeoff and landing procedures, is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation, ultimately enhancing your overall experience.
Navigation and Flight Planning
Effective navigation and flight planning are crucial for efficient and safe drone operation, especially for complex missions. Utilizing onboard systems and pre-flight planning significantly reduces the risk of errors.
Sample Flight Plan for Aerial Photography
A simple aerial photography mission might involve capturing images of a building from various angles. A sample flight plan could include:
- Waypoint 1: Initial takeoff point. Altitude: 50 meters. Speed: 5 m/s.
- Waypoint 2: Position above the building’s front. Altitude: 70 meters. Speed: 2 m/s (for detailed shots).
- Waypoint 3: Position above the building’s side. Altitude: 70 meters. Speed: 2 m/s.
- Waypoint 4: Position above the building’s rear. Altitude: 70 meters. Speed: 2 m/s.
- Waypoint 5: Return to takeoff point. Altitude: 50 meters. Speed: 5 m/s.
GPS and Onboard Navigation Systems
Most drones utilize GPS for navigation, allowing for precise positioning and autonomous flight. Some drones also include obstacle avoidance systems and other advanced navigation features.
Navigation Challenges and Solutions
Potential challenges include GPS signal loss, wind interference, and unexpected obstacles. Solutions include selecting appropriate flight modes, flying in areas with strong GPS signals, and utilizing obstacle avoidance features (if available).
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera settings and mastering image composition are essential for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. Experimentation and practice are key to developing proficiency.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO significantly impact image quality. Adjusting these settings based on lighting conditions is crucial for optimal results.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens, affecting depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light, affecting motion blur.
- ISO: Controls the sensor’s sensitivity to light, affecting image noise.
Optimal Image Composition and Framing
Achieving aesthetically pleasing images requires careful attention to composition and framing. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry are useful compositional techniques.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Different drone camera modes offer various creative possibilities. Experiment with different settings and modes to find what works best for your desired outcome.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure its continued reliable operation. These steps are crucial for maintaining the drone’s functionality and safety.
Safe Storage and Maintenance
After each flight, store the drone in a clean, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Regularly inspect and clean the drone, paying particular attention to the propellers, camera lens, and gimbal.
Common Drone Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance involves cleaning the drone body and propellers, checking for loose parts, and properly storing and charging the batteries. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery care is crucial.
Troubleshooting Potential Problems
Common issues include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor malfunctions. Addressing these issues promptly prevents more significant problems.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before the next flight.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with a stronger signal.
- Motor Malfunction: Inspect the motors for damage and contact support if necessary.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally and responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations and airspace restrictions. This ensures safe and lawful operation.
Relevant Regulations and Laws

Regulations vary by region. Familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations in your area regarding drone operation, including registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and permitted flight areas.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
In many regions, permits or licenses are required for commercial drone operation. Check with your local aviation authority to determine the necessary documentation for your specific use case.
Airspace Restrictions and Identification
Airspace restrictions, such as those near airports or other sensitive areas, must be respected. Utilize online resources and apps to identify restricted airspace before flying.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Mastering advanced drone techniques enhances your piloting skills and opens up creative possibilities for aerial photography and videography. Practice and patience are key to achieving proficiency.
Precise Hovering and Smooth Transitions, How to operate a drone
Precise hovering and smooth transitions between different flight maneuvers are crucial for capturing professional-quality footage. Practice these techniques in a safe, open area.
Complex Camera Movements
Advanced camera movements, such as smooth panning, tilting, and orbiting, add dynamism and visual interest to your aerial footage. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best.
Using Drone Accessories
Various accessories, such as gimbals, ND filters, and polarizing filters, enhance the quality and creative possibilities of your drone footage. Understanding their functions and applications is beneficial.
Drone Photography and Videography Best Practices
Creating cinematic drone shots requires a combination of technical skill and artistic vision. Careful planning and execution are crucial for achieving professional-quality results.
Achieving Cinematic Drone Shots
Cinematic shots often involve smooth, deliberate movements, creative camera angles, and thoughtful composition. Experiment with different techniques to find your style.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible drone piloting requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations.
Importance of Light and Composition
Light and composition are fundamental elements of photography and videography. Understanding how to use light effectively and applying strong compositional techniques is essential for compelling visuals.
Planning and Executing Drone Projects
A successful drone project requires careful planning, including location scouting, flight planning, and shot list creation. Thorough preparation minimizes on-site challenges and maximizes efficiency.
Mastering drone operation is a journey that combines technical skill with a deep understanding of safety and regulations. This guide has provided a solid foundation, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently pilot your drone and capture stunning visuals. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot. As you gain experience, explore advanced techniques and push your creative boundaries, always remembering to prioritize safety and responsible operation.
The sky’s the limit—but always fly within the legal and safe limits.
FAQ Overview
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for drones with obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functions.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in windy conditions or with heavy camera use.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately if you lose signal. If your drone doesn’t have RTH, try to maintain visual contact and carefully guide it back.
How do I clean my drone properly?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe the drone body. Avoid using water or harsh chemicals. For more stubborn dirt, use a slightly damp cloth.
